python tutorial - Python object serialization : yaml and json - learn python - python programming
What is yaml?
- YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language) is a human-readable data serialization language. It is commonly used for configuration files, but could be used in many applications where data is being stored (e.g. debugging output) or transmitted (e.g. document headers).
sample code
---
receipt: Oz-Ware Purchase Invoice
date: 2012-08-06
customer:
given: Dorothy
family: Gale
items:
- part_no: A4786
descrip: Water Bucket (Filled)
price: 1.47
quantity: 4
- part_no: E1628
descrip: High Heeled "Ruby" Slippers
size: 8
price: 100.27
quantity: 1
bill-to: &id001
street: |
123 Tornado Alley
Suite 16
city: East Centerville
state: KS
ship-to: *id001
specialDelivery: >
Follow the Yellow Brick
Road to the Emerald City.
Pay no attention to the
man behind the curtain.
...- strings do not require quotations. The specific number of spaces in the indentation is unimportant as long as parallel elements have the same left justification and the hierarchically nested elements are indented further. The sample above defines:
- An associative array with 7 top level keys
- The "items" key contains a 2-element array (or "list")
- Each element of which is itself an associative array with differing keys.
- Relational data and redundancy removal are displayed:
- The "ship-to" associative array content is copied from the "bill-to" associative array's content as indicated by the anchor (&) and reference (*) labels.
- Optional blank lines can be added for readability.
- Multiple documents can exist in a single file/stream and are separated by "---".
- An optional "..." can be used at the end of a file (useful for signaling an end in streamed communications without closing the pipe).
YAML vs JSON?
- Technically YAML is a superset of JSON. This means that, in theory at least, a YAML parser can understand JSON.
yaml validation
- We can use YAML Lint to validate *.yml file.
jason to yaml conversion
- Let's convert the following json to yaml:
{
"foo": "bar",
"baz": [
"qux",
"quxx"
],
"corge": null,
"grault": 1,
"garply": true,
"waldo": "false",
"fred": "undefined",
"emptyArray": [],
"emptyObject": {},
"emptyString": ""
}click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
Python code:
import json
import yaml
sample = {
"foo": "bar",
"baz": [
"qux",
"quxx"
],
"corge": None,
"grault": 1,
"garply": True,
"waldo": "false",
"fred": "undefined",
"emptyArray": [],
"emptyObject": {},
"emptyString": ""
}
json_obj = json.dumps(sample)
print 'json_obj =', json_obj
ff = open('data.yml', 'wb')
yaml.dump(sample, ff, default_flow_style=False)
ydump = yaml.dump(sample, default_flow_style=False)
print 'ydump=',ydumpclick below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
Output:
json_obj = {"emptyObject": {}, "emptyString": "", "emptyArray": [], "corge": null, "waldo": "false", "grault": 1, "garply": true, "foo": "bar", "baz": ["qux", "quxx"], "fred": "undefined"}
ydump= baz:
- qux
- quxx
corge: null
emptyArray: []
emptyObject: {}
emptyString: ''
foo: bar
fred: undefined
garply: true
grault: 1
waldo: 'false'click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
- If we open the data.yml :
baz:
- qux
- quxx
corge: null
emptyArray: []
emptyObject: {}
emptyString: ''
foo: bar
fred: undefined
garply: true
grault: 1
waldo: 'false'click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
- We can check our conversion is correct via yamllint:
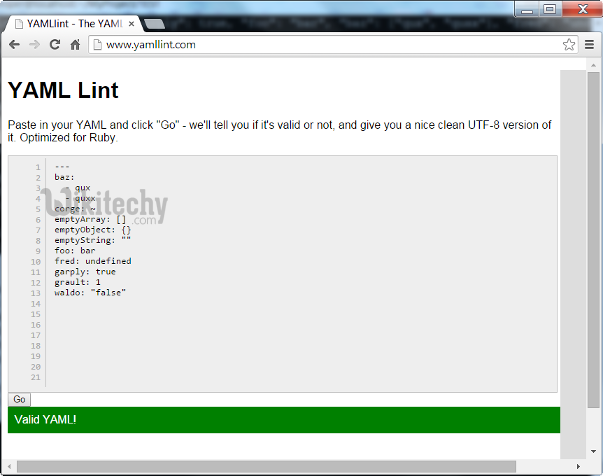
Learn python - python tutorial - python-yamllint - python examples - python programs
- We can reads in the yaml and write it to json:
stream = file('data.yml', 'r')
yml_loaded = yaml.load(stream)
with open('data.json','wb') as f:
json.dump(yml_loaded, f)click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
- The data.json looks like this:
{"emptyObject": {}, "emptyArray": [], "waldo": "false", "baz": ["qux", "quxx"], "emptyString": "", "corge": null, "grault": 1, "garply": true, "foo": "bar", "fred": "undefined"}click below button to copy the code. By Python tutorial team
- We can check the conversion using one of the online conversion tools:

Learn python - python tutorial - yml to json - python examples - python programs
